Choosing between Computed Radiography (CR) and Digital Radiography (DR) can feel like a tough decision. Both are modern X-ray technologies that have moved beyond traditional film-based systems, but they function differently and come with their own sets of benefits and challenges. This guide breaks down the differences and considerations to help you choose the best option for your facility.
X-Ray Imaging Systems: Comparing CR and DR
Computed Radiography (CR)
CR uses phosphor plates to capture X-rays. After exposure, the plates must be processed through a reader to convert the image into a digital format. This extra step can slow down the workflow but still provides reliable diagnostic images.
Digital Radiography (DR)
DR, on the other hand, captures X-ray images directly using digital detectors. These detectors instantly transmit the image to a connected computer for immediate viewing. This streamlined process eliminates the need for cassettes and significantly speeds up image acquisition in x-ray imaging systems.
Key Differences in Radiology Workflow and Imaging Technology
Let’s dive deeper into the specific areas where CR and DR differ, highlighting what to consider when deciding between the two:
1. Image Acquisition Process
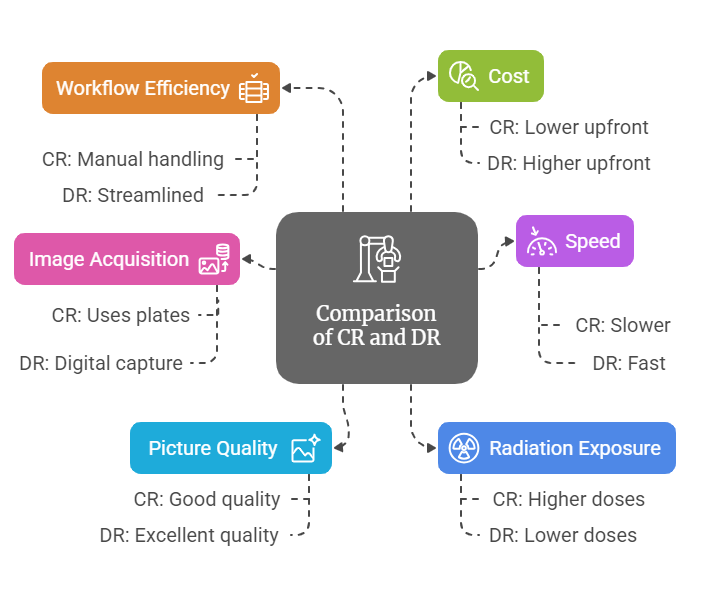
- CR: Phosphor plates need to be processed through a reader before images are available. This typically takes 1-2 minutes per image, slowing the workflow for high-volume facilities.
- DR: Offers immediate image preview within 5-10 seconds thanks to direct digital capture. This rapid image availability makes it ideal for busy practices or emergency scenarios.
2. Image Quality
- DR: Generally produces better images due to higher detective quantum efficiency (DQE), which means it can capture more X-ray energy for clearer, sharper pictures. It also provides:
- Better contrast resolution, making subtle differences in tissue density easier to detect.
- Lower noise levels, ensuring images are clean and accurate.
- CR: While CR can still deliver diagnostic-quality images, it may require more post-processing to achieve similar clarity to DR.
3. Radiation Dose Efficiency
- DR: Uses 30-50% less radiation than CR systems for comparable image quality, making it safer for patients, especially children.
- Modern DR detectors are designed with better dose efficiency, further enhancing patient safety.
- CR: Requires higher doses of radiation to capture similar-quality images, which can be a concern for pediatric or repeat imaging needs.
4. Workflow Efficiency
- CR: Requires manual handling of cassettes and processing through a reader. This adds to the overall time per patient and reduces throughput.
- DR: Enhances workflow by eliminating cassette handling and delivering images instantly. Its immediate image verification also reduces the chances of repeat exposures.
- DR systems integrate seamlessly with Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS), streamlining radiology workflow optimization by enabling faster image sharing and storage.
5. Durability and Maintenance
- CR: Phosphor plates need regular replacement, typically every 2-3 years, which adds to ongoing costs. However, CR systems generally have fewer electronic components, so there’s less risk of major failures.
- DR: Digital detectors are more durable and require less frequent replacement. However, if repairs are needed, they can be expensive. This makes maintenance costs a key consideration for facilities with tight budgets.
Why Choose Computed Radiography (CR)?
CR still holds its place as a practical choice for certain facilities. Here’s why you might opt for CR:
- Lower Upfront Costs CR systems are more affordable initially, making them accessible for smaller clinics or facilities with limited budgets.
- Portability and Flexibility CR systems rely on cassettes, which are portable and easy to use across multiple rooms or mobile setups.
- Familiar Workflow For teams transitioning from film-based systems, CR offers a more gradual adjustment, as the workflow is similar to traditional methods.
- Reliable for Low-Volume Use If your facility handles a small number of patients daily, CR’s slower processing time is less of a concern.
Why Choose Digital Radiography (DR)?
DR is increasingly becoming the gold standard for modern healthcare facilities. Here’s why it stands out:
- Faster Workflow With images ready in 5-10 seconds, DR enhances workflow efficiency and increases patient throughput in busy healthcare settings, making it ideal for busy clinics, hospitals, or emergency departments.
- Sharper Image Quality DR’s superior clarity and resolution help detect subtle abnormalities, improving diagnostic accuracy.
- Safer for Patients By using significantly less radiation, DR enhances patient safety, especially for pediatric imaging or patients requiring frequent X-rays.
- Seamless Integration Modern DR systems connect easily to PACS, streamlining image sharing and storage for better collaboration between departments.
- Long-Term Cost Efficiency While DR systems require a larger upfront investment, their minimal maintenance needs and faster workflow save money over time.
What’s the Best Option for You?
When choosing between CR and DR, think about the specific needs and goals of your facility. Consider these questions:
- Is budget your primary concern?
- Do you handle a high volume of patients daily?
- Are you focused on minimizing radiation exposure?
- How important is long-term cost efficiency?
Go with CR if:
- You have a limited budget and need a cost-effective solution.
- Your clinic handles fewer patients, so speed isn’t critical.
- You need a system that’s portable and works in various settings.
- You want a familiar workflow that’s easy to adopt.
Go with DR if:
- Your facility needs fast image acquisition to keep up with high patient volume.
- You prioritize safety with reduced radiation exposure.
- Long-term savings and efficiency matter more than initial costs.
- You want top-notch image quality for better diagnostic outcomes.
Real-Life Examples: How CR and DR Work in Practice
Case 1: A Rural Clinic Using CR
A small rural clinic with a limited budget opted for a CR system. With only a few patients each day, the slower processing time didn’t cause delays. The portability of the cassettes made CR an excellent choice for their portable X-ray system needs, allowing them to use one system across different departments. For their needs, CR was the perfect fit.
Case 2: A Busy Urban Hospital with DR
In a large hospital handling hundreds of patients daily, a DR system proved invaluable. The instant image processing provided by DR, a key aspect of medical imaging technology, reduced patient wait times and helped doctors diagnose and treat cases more efficiently. The lower radiation doses were particularly beneficial for pediatric and repeat patients.
Tips for Transitioning from CR to DR
If your facility currently uses CR but is considering upgrading to DR, here are some tips to make the switch smoother:
- Train Your Staff
Ensure your team understands the new system and its features. Hands-on training can help staff feel confident in operating DR systems. - Start Small
Begin with a single DR unit in one department to see how it integrates with your workflow before rolling it out facility-wide. - Evaluate Costs
While DR requires a higher upfront cost, calculate the potential savings in labor, cassette replacements, and reduced downtime—key factors in evaluating the cost of radiography systems. - Leverage Advanced Features
Take advantage of DR’s modern tools, like wireless imaging and automatic beam detection, to streamline operations and improve efficiency. - Seek Vendor Support
Many DR system vendors offer ongoing support and training programs, ensuring a smooth transition and addressing any technical issues quickly.
CR vs. DR: The Big Picture
CR and DR each have unique strengths. CR is great for smaller practices, mobile imaging, or clinics prioritizing affordability and portability. DR, on the other hand, is ideal for facilities focused on speed, image quality, and patient safety.
As advancements in healthcare technology continue, DR is becoming the standard for most facilities, offering a seamless blend of speed, efficiency, and safety. But CR remains a practical option for those with specific needs. Whatever you choose, the goal is to deliver accurate, efficient care to your patients.
Bottom Line
Deciding between CR and DR depends on your facility’s priorities, from budget and patient volume to image quality and workflow efficiency. CR offers a reliable and budget-friendly solution for smaller or low-volume practices, while DR shines in high-demand settings with its speed, clarity, and safety advantages.
With the insights from this guide, you can confidently choose the system that best aligns with your goals and delivers top-quality care.