Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) represents a significant advancement in dental imaging technology. While traditional Medical Computed Tomography (CT) scanners have long been used for diagnostic purposes, CBCT scanners offer specialized advantages for dentistry and maxillofacial imaging. This article explores what CBCT scans are, how they work, their practical applications, and how they compare to traditional CT scanners.
What is a CBCT Scan?
CBCT is an advanced imaging technology designed to capture highly detailed, three-dimensional (3D) images of the oral and maxillofacial structures. Unlike traditional X-rays, which produce only two-dimensional (2D) images, CBCT scans compile over 150 images taken from various angles around the patient’s head into a comprehensive 3D representation. This allows for precise visualization of:
- Teeth
- Bones
- Nerves
- Soft tissues
CBCT scanners have revolutionized diagnostic capabilities in dentistry, enabling more accurate evaluations and treatment planning. With its ability to provide unparalleled detail, CBCT is often considered an essential tool in complex dental cases.
How Does a CBCT Scan Work?
The CBCT scanning process is straightforward and non-invasive, involving three main steps:
1. Preparation
Patients are asked to remove any metal objects, such as jewelry or dental appliances, to avoid interference with imaging. If there is any possibility of pregnancy, this should be communicated to the dental professional to ensure safety. Patients are also advised to stay still during the scan for the best results.
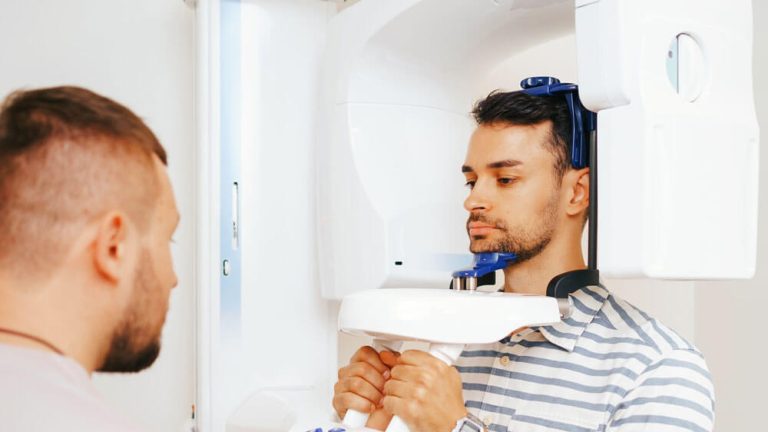
2. Positioning
The patient is positioned in the CBCT machine, either sitting or standing. Chin supports or ear stabilizers are often used to ensure stability during the scan. This simple setup makes CBCT scanning accessible to patients of all ages, from children to older adults.
3. Scanning Process
The CBCT machine rotates around the patient’s head, capturing multiple images from various angles. This process typically lasts less than a minute, producing a detailed 3D image without any discomfort. Once the scan is complete, the data is processed into a digital 3D model that dental professionals can analyze.
CBCT Scans vs. Medical CT Scans: Key Differences
While both CBCT and medical CT scanners are valuable imaging tools, they have distinct differences that make CBCT particularly suited for dental and maxillofacial applications.
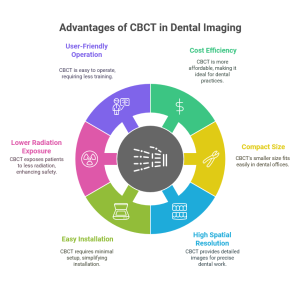
1. Cost Efficiency
CBCT scanners are significantly more affordable, costing approximately 3 to 5 times less than traditional CT scanners. This affordability makes them ideal for use in dental offices and outpatient facilities, where cost-effective solutions are crucial.
2. Equipment Size and Weight
CBCT scanners are smaller and lighter, allowing them to fit comfortably in dental offices or clinics without requiring significant space adjustments. This compact design ensures they can be installed in a wide range of healthcare settings.
3. Spatial Resolution
CBCT scanners offer superior spatial resolution with smaller pixel sizes, providing highly detailed images. This makes them particularly effective for visualizing dental and jaw structures, where precision is critical for treatments such as dental implants and orthodontics.
4. Installation Requirements
CBCT scanners require minimal setup compared to medical CT scanners:
- They can operate in standard office environments without needing a controlled (cold) temperature.
- They do not require high-capacity electrical systems or special floor reinforcements, making installation more accessible.
These reduced requirements make CBCT scanners more convenient for dental practices looking to expand their diagnostic capabilities.
5. Radiation Exposure
CBCT scans expose patients to significantly lower radiation levels compared to traditional CT scans:
- Traditional CT scans equate to 63–154 days of background radiation exposure.
- CBCT scans range from 6–30 days of background radiation, making them safer for repeated use.
This lower dose of radiation makes CBCT an excellent option for children and patients who may require multiple scans over time.
6. Ease of Operation
CBCT scanners are simpler to operate, requiring less technical expertise than medical CT scanners. This ensures dental professionals can use them efficiently without specialized training. As a result, CBCT has become a preferred tool for general dentists and specialists alike.
Why is a CBCT Scan Important?
CBCT scans are invaluable in modern dentistry and maxillofacial imaging due to their precision, versatility, and ability to improve patient outcomes. Here’s why you might need a CBCT scan:
1. Precise Diagnosis and Treatment Planning
The detailed 3D imaging provided by CBCT allows dental professionals to:
- Detect hidden infections.
- Evaluate bone structure for dental implants.
- Plan orthodontic treatments with greater accuracy.
For example, CBCT can reveal previously undetected bone deficiencies or irregular tooth roots that could complicate routine procedures.
2. Enhanced Patient Understanding
3D images help patients visualize their dental conditions and treatment plans, fostering informed decision-making and building trust in their care. For instance, showing a 3D view of a potential dental implant site can help patients better understand why the procedure is necessary.
3. Versatile Applications
CBCT scans play a key role in various dental procedures, including:
- Dental Implants
CBCT scans provide critical information about bone density and structure, ensuring accurate implant placement and long-term success. They also help identify potential risks, such as proximity to nerves or sinuses.
- Orthodontics
Detailed imaging aids in planning complex tooth movements and alignments, improving orthodontic treatment outcomes. CBCT is particularly valuable in cases involving impacted teeth or jaw discrepancies.
- Endodontics
CBCT helps diagnose challenging root canal issues by visualizing curved root structures and surrounding tissues. It is especially useful in identifying infections or fractures that are difficult to detect with traditional X-rays.
4. Identification of Dental Issues
A single CBCT scan can uncover a range of problems, such as:
- Tooth decay
- Bone loss
- Periodontal infections
- Abnormal growths
- Facial fractures
- Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) issues
This comprehensive imaging capability reduces the need for additional diagnostic tests, saving both time and money.
Common Questions About CBCT Scans
1. What is the difference between CBCT and traditional X-rays?
CBCT creates 3D images that provide much more detail than traditional 2D X-rays. This makes CBCT ideal for diagnosing complex dental and maxillofacial issues that may not be visible on standard X-rays.
2. Is a CBCT scan safe?
Yes, CBCT scans are safe and use lower radiation doses compared to traditional CT scans. The radiation exposure from a CBCT scan is roughly equivalent to 6–30 days of natural background radiation.
3. How long does a CBCT scan take?
The scanning process is quick and painless, typically lasting less than a minute. This makes CBCT a convenient option for both patients and dental professionals.
4. What can a CBCT scan detect?
CBCT scans can detect hidden infections, evaluate bone density for implants, plan orthodontic treatments, and diagnose issues like tooth decay, bone loss, TMJ problems, and more.
5. Do all dental offices have CBCT scanners?
Not all dental offices have CBCT scanners, as they are specialized equipment primarily used in practices offering advanced dental procedures like implants, orthodontics, or endodontics. However, many modern dental clinics are adopting CBCT technology for its diagnostic benefits.
Wrap-up
CBCT scans are a transformative tool in dental and maxillofacial imaging. By combining high-quality 3D imaging with minimal radiation exposure, CBCT scanners provide safer, more efficient, and more accurate diagnostic capabilities than traditional CT scanners. Their versatility makes them an essential part of modern dental practices, enabling precise treatment planning and improved patient outcomes.