What Is a Flat Panel Detector?
A flat panel detector (FPD) is a modern device mainly used in digital X-ray imaging. These detectors convert X-ray signals into digital images, which are crucial for diagnosing health problems. FPDs enable doctors to view and analyze X-ray images immediately on computers, making it easier to make quick medical decisions.
What Are The Different Types of Flat Panel Detectors?
Direct Conversion Flat Panel Detectors
Direct conversion flat panel detectors use a special material called a photoconductor, usually made from amorphous selenium or cadmium telluride. These detectors convert X-rays directly into electric charges. By skipping the step of turning X-rays into light, they produce clearer images. This makes them ideal for specific uses like mammography.
Indirect Conversion Flat Panel Detectors
Indirect conversion flat panel detectors first change X-rays into visible light using a scintillator, which is often made from materials like cesium iodide or gadolinium oxysulfide. Then, an array of photodiodes detects this light and turns it into an electrical signal. This type is commonly used in general X-ray exams and fluoroscopic imaging because it provides excellent image quality.
CMOS and CCD Flat Panel Detectors
- CMOS Flat Panel Detectors: These detectors use complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor technology to capture images. They are known for using less power and can capture images quickly.
- CCD Flat Panel Detectors: Charge-coupled device detectors also capture light and convert it into an electrical charge. They offer high-quality images but can be bulkier and more expensive than other types.
What Are Flat Panel Detectors Made Of?
Flat panel detectors consist of several important parts that work together to create clear images:
Indirect FPD Components:
- Scintillation Layer: This layer contains special materials that turn X-ray radiation into visible light.
- Photodiode Array Layer: This part changes the light signals from the scintillator into electrical signals.
- Thin-Film Transistor (TFT) Array: This amplifies the electrical charges to prepare them for creating the final image.
Direct FPD Components:
- Photoconductive Layer: Made of amorphous selenium, this layer generates electrical charges directly when X-rays hit it.
- High-Voltage Electrodes: These collect the electrical charges and help keep the charges from recombining.
- TFT Array: This reads the charges to create the final image.
How a Flat Panel Detector Works
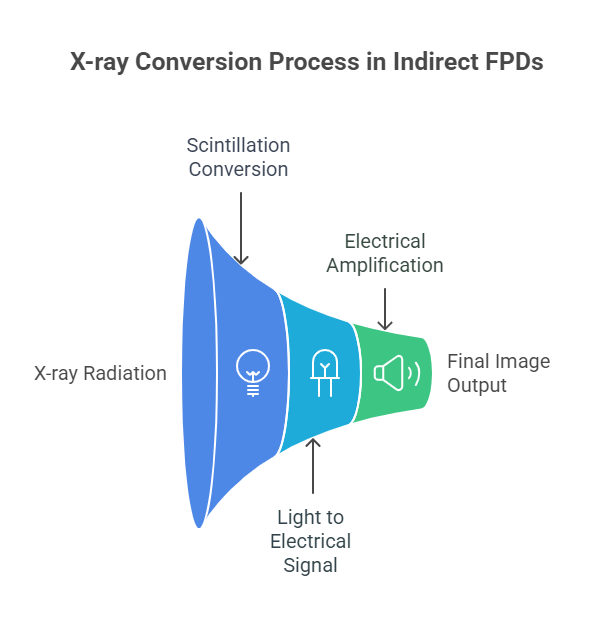
Indirect Conversion:
- X-ray photons hit the scintillator, creating visible light.
- Amorphous silicon photodiodes detect this light and create an electrical signal based on how much light they receive.
- The signal is amplified and processed using TFT technology to make a digital image.
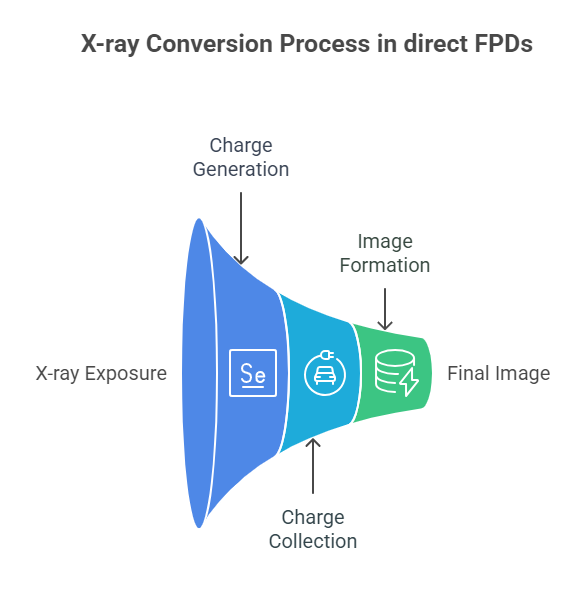
Direct Conversion:
- When X-ray photons strike the photoconductor, they create electron-hole pairs.
- The electrodes collect these charges, creating a current that reflects the X-ray exposure.
- This current is read out by TFTs to create a digital image.
Comparing Traditional X-ray Systems and FPDs
| Feature | Traditional X-ray Systems | Flat Panel Detectors |
| Image Processing Time | Minutes to hours (chemical processing) | Immediate (digital) |
| Image Storage | Physical films | Digital files |
| Image Quality | Good but fixed | Excellent and adjustable |
| Radiation Dose | Higher | Lower |
| Environmental Impact | Chemical waste | Minimal waste |
| Operating Costs | Ongoing film and chemical costs | Higher initial cost, lower long-term costs |
Applications of Flat Panel Detectors
Flat panel detectors have found their way into various fields:
Medical Applications:
- General radiography for bones and chest X-rays
- Dental imaging for detailed tooth and jaw pictures
- Mammography for breast cancer screening
- Fluoroscopy for real-time imaging during procedures
Industrial and Security Uses:
- Quality control in manufacturing
- Airport security screening
- Building and bridge inspection
- Scientific research and experiments
Advantages of Flat Panel Detectors
These modern detectors offer significant benefits over traditional X-ray systems, making them increasingly popular in healthcare and other fields:
- Better Image Quality: The images are sharper and clearer, helping doctors spot small details they might miss otherwise. Think of it like switching from an old TV to a new HD screen – the level of detail is dramatically better. These detectors can show subtle differences in tissue density, which helps doctors make more accurate diagnoses.
- Quick Results: No more waiting around. As soon as the X-ray is taken, doctors can see it on their computers. Remember the days of waiting for photos to develop? This is like having a digital camera instead – you see results right away. This means doctors can quickly check if they got a good image and take another if needed.
- Less Radiation: These detectors need less X-ray power to get good images. This is great news, especially for kids who need X-rays. It’s like getting the same quality photo with less light – the new technology is just that much better at capturing what it needs to see.
- Saves Money Over Time: While getting started costs more, hospitals end up saving money. They don’t need to buy film or chemicals anymore, and they don’t need large rooms to store all those X-ray films. Everything’s stored on computers now.
- Easy to Adjust Images: Doctors can make the pictures brighter or darker after they’re taken, just like editing a photo on your phone. If something’s hard to see, they can adjust it without having to take another X-ray.
- Better for Patients: The whole process is faster, which means less time lying still on the X-ray table. This makes a big difference for people who are in pain or have trouble staying still. One quick snap, and they’re done!
- Good for the Environment: No more chemical waste from developing films. It’s like switching from film cameras to digital – better pictures and better for our planet.
The Impact and Future of FPD Technology
With all these advantages and applications, flat panel detectors have become essential tools in modern imaging. Let’s look at what this means for the future of this technology.
Wrap-up
Flat panel detectors have transformed medical imaging and beyond. From hospitals to airports, these devices have made X-ray imaging faster, safer, and more reliable. They help doctors make quicker, more accurate decisions while keeping radiation exposure low.
The technology continues to improve, just like how smartphone cameras get better each year. Newer versions produce clearer images while using even less radiation. As healthcare becomes more digital, these detectors will play an even bigger role in patient care.
But it’s not just about the technology – it’s about making a real difference in people’s lives. Whether it’s helping diagnose health problems earlier or making security screenings more efficient, flat panel detectors are improving our world in practical, meaningful ways.
Need help choosing a flat panel detector for your practice? Our expert team can guide you through our selection and flexible payment plans to find your perfect match.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How long do flat panel detectors typically last?
With proper care and maintenance, flat panel detectors usually last 5-7 years of regular use. However, their lifespan can vary depending on usage patterns and maintenance quality.
Can flat panel detectors be repaired if damaged?
Yes, many components can be repaired by qualified technicians. However, damage to the detector panel itself often requires replacement of the entire panel due to its sensitive nature.
How much training do healthcare workers need to use FPDs?
Most healthcare workers can learn to operate FPD systems within a few days. The interface is usually intuitive, similar to using digital photography equipment, though understanding all image optimization features may take additional training.
What are the power requirements for FPD systems?
Most modern FPD systems operate on standard hospital power supplies. CMOS-based systems typically use less power than CCD-based ones, making them more energy-efficient.
Can FPD images be shared between different healthcare facilities?
Yes, FPD images can be easily shared through secure medical imaging networks (PACS – Picture Archiving and Communication Systems), allowing for remote consultations and second opinions.