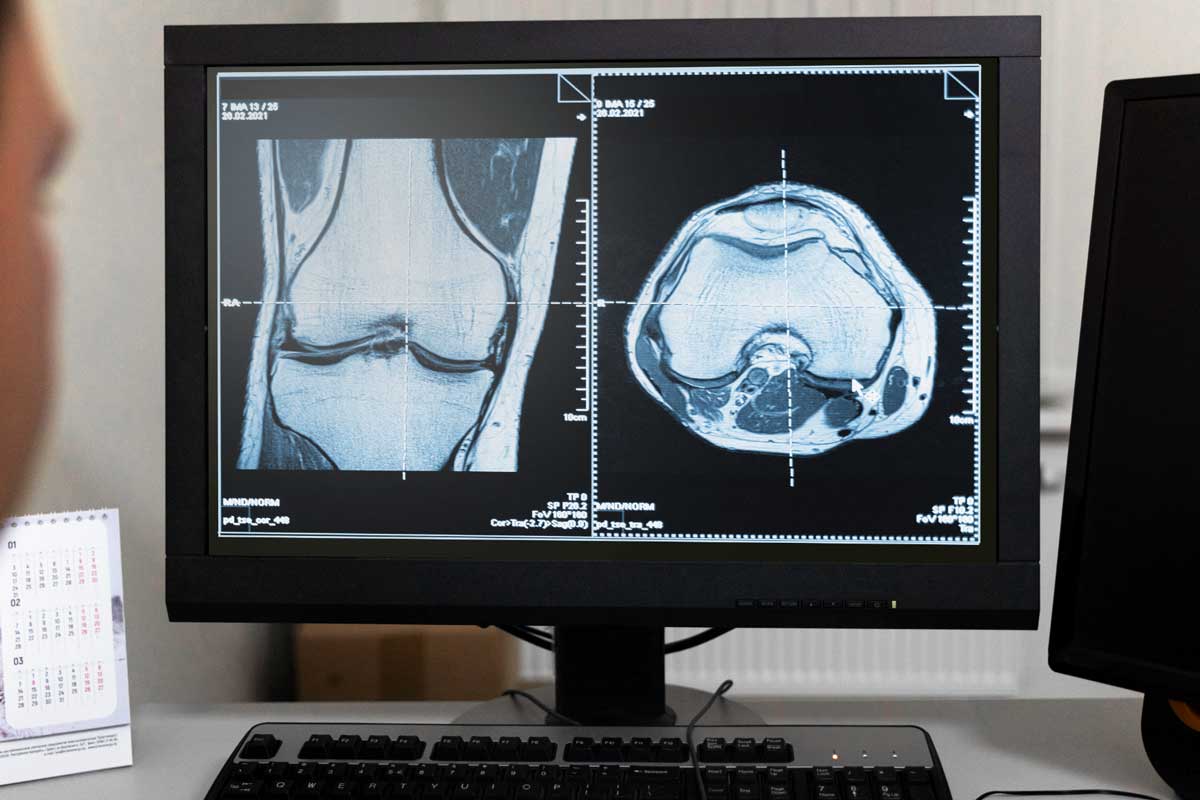
One of the most significant developments in contemporary medical diagnostics is radiography. Nowadays, a lot of medical procedures are necessary.
This changing industry is crucial. It aids in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of numerous medical diseases. In medicine, radiography has become an essential tool for anything from detecting fractures to assisting with cancer therapies.
The fundamentals of radiography will be covered in this essay. We’ll examine its various applications and the crucial function that radiologists play. The advantages and disadvantages of radiography will also be covered. Let’s explore this fascinating field in more detail.
Radiography: What Is It?
One subfield of medical imaging is radiography. It makes use of electromagnetic energy in the form of X-rays. This method produces finely detailed pictures of the human body’s inside.
This diagnostic imaging technique makes use of the different speeds at which different biological tissues absorb X-rays. Bones and other dense materials absorb more X-rays. As a result, they appear as white on an X-ray picture. Softer tissues seem darker and absorb less X-rays.
One non-invasive method of seeing within the body is radiography. There is a vital tool for tracking and diagnosing a wide range of medical issues. Over time, the technology has undergone tremendous change, spanning two main approaches:
- Standard radiography Using photographic film, pictures are taken using this older technique. Newer methods eventually replace it, albeit they are still effective.
- Digital radiography: A more sophisticated method that uses an electronic device to take pictures. Higher image quality, quicker processing times, and noticeably less radiation exposure are just a few benefits of digital radiography that enhance productivity and patient safety.
From diagnosing lung disorders and fractures to assisting in the therapy of cancer, radiography has many uses. In radiation therapy, it serves a therapeutic purpose as well. Accurate imaging aids in locating cancerous cells while preserving surrounding healthy tissues.
The Various Uses of Radiography in Healthcare
Because of its adaptability, radiography is used in many different medical specialties. These are a few of its most crucial and widespread applications:
1. Recognizing orthopedic disorders and bone fractures
Orthopedics is one of the oldest and most established applications of radiography.
- Bone Fractures: X-rays are useful in determining the type, locati0n, and severity of fractures.
- Chronic Joint Disorders: Osteoporosis and arthritis can be monitored using radiography. It helps assess bone density and joint health.
- Aftercare Surveillance: To determine whether bone fractures are mending properly, doctors utilize X-rays. They also aid in evaluating the effectiveness of orthopaedic operations.
2. Evaluating respiratory and chest conditions
Chest X-rays are still essential for medical diagnosis, especially when it comes to detecting heart and lung disorders. Typical applications include of:
- Diagnosing pneumonia: identifying lung infections.
- Heart Conditions: Evaluating anomalies or indications of heart failure.
- Lung Diseases: Recognizing tuberculosis, persistent obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and lung cancer.
- Post-Treatment Progress Monitoring: Assessing how well pulmonary treatments are working.
3. Imaging of the teeth
In dentistry, radiography is essential for diagnosing and treating problems related to oral health:
- Identifying abscesses, gum disease, and tooth decay.
- Recognizing issues with wisdom teeth or impacted teeth.
- Assessing the effectiveness of orthodontic or oral surgery procedures.
Clear views of teeth, gums, and surrounding bone are provided by dental X-rays, such as bitewing or panoramic varieties. This aids in precise therapy planning.
4. Using mammography to identify breast cancer early
A specific type of radiography called mammography is only used to image the breasts. Its main objective is the early identification of breast cancer, which includes: • Finding anomalies and tumors early on.
- Checking for microcalcifications, which may indicate cancer in its early stages.
- Monitoring the effects of treatment on patients receiving therapy for breast cancer.
Regular mammograms are an essential preventive measure that, when performed early, greatly increases survival rates.
5. Directing surgical techniques
By giving surgeons access to real-time imagery, radiography helps them execute intricate surgeries with accuracy.
- Orthopedic Surgery: Making sure that implants and bones line up correctly during operations like joint replacements.
- Catheter Placements: Precisely directing stents or catheters during vascular or cardiac procedures.
- Minimally Invasive Surgeries: Assisting in the instrument placement with the least amount of tissue damage possible.
6. Trauma and emergency care
Time is of the essence in emergency situations, and radiography is essential for quick diagnosis. X-rays are frequently the initial course of treatment for trauma patients in order to: • Identify internal injuries, fractures, and dislocations.
- Find alien items that are ingrained in the body.
- Make it easier to make quick decisions about interventions that could save lives.
Radiographers’ Function in Medical Imaging
Every excellent radiography image is the result of a trained radiographer’s work. Radiologic technicians, another name for radiographers, are highly skilled individuals who operate the advanced imaging equipment used in radiography. Among their duties are:
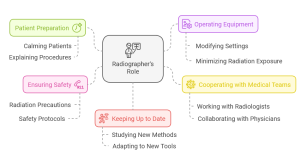
- Patient Preparation: Radiographers make sure patients are at ease and in the right position for imaging tests. This frequently entails calming the patient’s fears and outlining the process.
- Operating Equipment: They modify the settings of the equipment to get the best pictures while exposing the least amount of radiation possible.
- Cooperating with Medical Teams: Radiologists and radiographers collaborate closely. Physicians who interpret medical images are known as radiologists. They work along with other medical professionals as well. Accurate diagnosis and treatment approaches are made possible by this collaboration.
- Ensuring Safety: Protecting against radiation is of utmost importance. Radiographers take precautions to avoid needless exposure for both themselves and their patients.
- Keeping Up to Date: Radiographers are constantly studying new methods and tools. Their field’s technology is constantly evolving.
Juggling the Benefits and Risks of Radiography
Despite the fact that radiography has transformed medical diagnosis, it is important to acknowledge both the hazards and the advantages it offers. Achieving this equilibrium guarantees that patients have the safest and most efficient treatment available.
Possible hazards in radiography
- Radiation Exposure: X-rays expose patients to ionizing radiation, which raises the risk of cancer in high doses. But thanks to recent developments, imaging radiation levels are now much lower.
- Pregnancy Concerns: X-rays can be harmful to the growing fetus during pregnancy, particularly in the first trimester. Thorough screening and alternate imaging methods, such as ultrasonography, are often the best options for pregnant patients.
- Contrast Media Allergies: To enhance image clarity, certain radiography techniques include contrast agents. Despite being generally safe, a tiny percentage of individuals may experience adverse reactions to these medications.
The advantages of radiography
Despite the risks, radiography is a vital component of contemporary healthcare since its advantages greatly exceed its disadvantages:
- Non-Invasive Imaging: Radiography offers a painless, non-invasive way to look at inside structures, in contrast to surgical investigation.
- Accurate and Timely Diagnoses: Accurate condition identification made possible by high-resolution imaging enables prompt action.
- Broad Versatility: Radiography is used in many different fields of medicine. These include dentistry, cardiology, cancer, and orthopedics.
- Treatment Guidance: Radiographic imaging improves results by ensuring precise targeting during operations like surgery or radiation therapy.
- Disease Monitoring: By monitoring the course of chronic illnesses and assessing the efficacy of treatment, radiography aids in long-term management.
Common Questions Regarding Radiography
1,Is it safe to do radiography?
Yes, radiography is regarded as safe by qualified experts who use contemporary equipment. Diagnostic imaging uses very low radiation doses, and precautions are taken to further limit exposure. Accurate diagnosis and treatment usually have more advantages than disadvantages.
2,Can patients get radiography while pregnant?
Radiography during pregnancy is generally avoided by doctors unless it is absolutely required. In order to protect the fetus, clinicians prefer alternative imaging techniques like ultrasound or MRI when they need imaging.
3,Do you know of any alternatives to x-rays?
Indeed, physicians may employ additional imaging techniques, such as CT, MRI, or ultrasound, based on the patient’s condition.
Final Thoughts
A vital component of contemporary medicine, radiography helps to bridge the gap between non-invasive diagnosis and efficient treatment planning. Radiography continues to be a vital tool for healthcare professionals as technological developments improve its precision and security.
New digital radiography equipment should be taken into consideration by practices who wish to utilize the newest technology. Both diagnosis and patient treatment may benefit from this. Radiographers who embrace innovation not only aid in the diagnosis of illnesses but also significantly enhance people’s lives.